Introduction of Social Media
Wake up in the morning and squint at the tiny blue screen in the hands of a sleepy young adult. Scrolling through the variety of posts, tweets, pictures, and videos to see what is going on in the lives of those they know. “Oh, sweet! My post is at 75 likes!” “What? How can he get over 100 favorites for posting about his dinner?!” “My sister is killing it for her job!” after pressing ‘like’ for the picture that shows she got employee of the month. Social media has become a way to connect with people we know and share our opinions on news and events occurring around the world. With the extension of picture and video media, social media is a great way of passing time similar to watching TV. Some of the most popular social media sites include Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, Reddit, Tinder, YouTube, Snapchat, the list goes on!
The variety of platforms allows for a wide range of uses and attracts users in a variety of ways. Facebook is popular because users can friend and follow others they know or like and keep up with the events going on in their lives. Twitter is the home of the #hashtag and a great place to follow people and read about events in a short and sweet way since tweets are limited to 140 characters. Instagram is a platform where all posts include a picture or video followed by a caption. Snapchat allows users to communicate with each other through pictures and videos that are seen once or twice and then go away forever. Each platform has its own unique interface, but they are all similar in being a public online space for users to connect and stay in touch.
Social media began through a variety of online platforms for users to share their interests and connect with others who shared similar interests. Then, it evolved into an online public space to connect and network with people. According to Boyd (2014), “social media refers to the sites and services that emerged during the early 2000s, including social networking sites, video sharing sites, blogging and microblogging platforms, and related tools that allow participants to create and share their own content” (p. 6). Additionally, social media enables people to interact in online communities (Boyd, 2014). It bridges the gap between not being able to physically be around people and wanting to connect with them.
History
The history of social media can, technically, be traced back to 1971 when the first e-mail was sent between two side-by-side computers. However, for the purpose of this book, the social media platforms covered will be those separate and beyond simple e-mail, which in this case began in 1997 with the inception of the website called Six Degrees. Its premise was to allow users to make their profiles and then friend others; the site was based on the “six degrees of separation” theory, and only last from 1997-2001. During this time, ICQ (I Seek You,) an open source instant messaging program went live, as well as America Online (AOL,) a web-browser and it’s instant messaging service, AIM.
By 2003 over 100 million people were online and using browsers for more than looking up information; online chatrooms were prevalent, where friends and relationships – platonic and romantic – were made. At this time, MySpace launched and it was just the first wave of social media platforms that would encourage people to do more than just chat online. MySpace was a site that aspiring musicians posted to, in hopes that not just the general public heard and liked their music, but also record producers to land musical contracts. LinkedIn is another platform that went live in that same year, and was aimed, and still is, at professionals looking to network, socialize and find jobs using one service to do it all.
MySpace inspired sites such as Facebook, which was initially launched in 2004 solely to Harvard students as TheFacebook.com. It didn’t take long for Zuckerberg to realize Facebook could be bigger and better and so released it to everyone online, as facebook.com. Two years later Twitter was launched, unique and distinct from Facebook by imposing a limit of 140 characters per tweet. Facebook is currently the number one social platform, world-wide, and more than 500 million users engage on Twitter.
By 2008 Facebook had basically made MySpace obsolete and was well on the way to dominating other social media platforms, though the genre is ever-changing. Flickr and Photobucket were both put out as photo sharing sites, with users given the capability to comment on uploaded images. Instagram was another service launched for sharing photography, with more emphasis on commenting on users uploads.
Between 2007 and 2010, multiple social media platforms went live, some with more success than others: Tumblr is less popular than Facebook appeals to a younger demographic of users, with people in their late teens to early/mid-twenties for the most part. Foursquare was popular for a while on smartphones, with the ability to “check-in” to locations and businesses, and sometimes receive coupons or free items for doing so. Google Buzz, Loopt, and Blippy were popular in their time, as well as Pinterest, and Spotify showing an ability to maintain their popularity with both new and old users.
By the late 2000’s, businesses had begun to realize that these different social media platforms were also prime spaces for advertisement; how odd is it, now in 2016, to come across a business that doesn’t have official Facebook and Twitter pages? There are hundreds, if not thousands of social media platforms and all cater to different demographics and core services.
More recently, and at a time when everyone and their mother had Facebook accounts, teenagers were looking for something other than that service to communicate with their friends and Snapchat arrived in 2011, just in time for the teen exodus from Facebook. Snapchat provided the ability for users to take pictures and videos known as “snaps,” use a number of different filters and effects, then send them to friends, and after being viewed would become inaccessible. Later updates included “stories” and “memories” where stories are viewed chronologically and memories allow users to save snaps to a private file for later viewing.
One year after Snapchat’s release, Vine, which was acquired by Twitter right before it was released to the public, launched and allows for six-second video clips to be taken or spliced together from different scenes, and is shareable via Facebook and Twitter, and can also be embedded on websites, such as Tumblr. Both Vine and Snapchat are massively popular with the younger demographic though like other social media platforms, businesses have begun using them for advertisements and promotions.
As this brief history shows, social media has only continued to gain steam since 1997 and MySpace with many platforms arriving, though some are more successful and see better longevity. Teenagers and young adults are one of the driving forces behind the creation of these multiple platforms and as long as this demographic continues to both be targeted and consume social media in such large numbers, new creators will continue to create platforms that reach such a broad audience.
Statistics
Social Media plays a role in a lot of people's lives some a much bigger role than others. Some people make their living using social media, whether that be using it for advertising for a business or being an entertainer. So how big of an impact does social media make? Well that's a hard question to answer with an exact answer, so in this section we will explore a few statistics that might give you a bigger picture of social media. We must also keep in mind that no study is perfect nor does it stay current for very long, so it should go without saying but all stats are only accurate at the time of writing this (October 2016). That being said let's get into it.
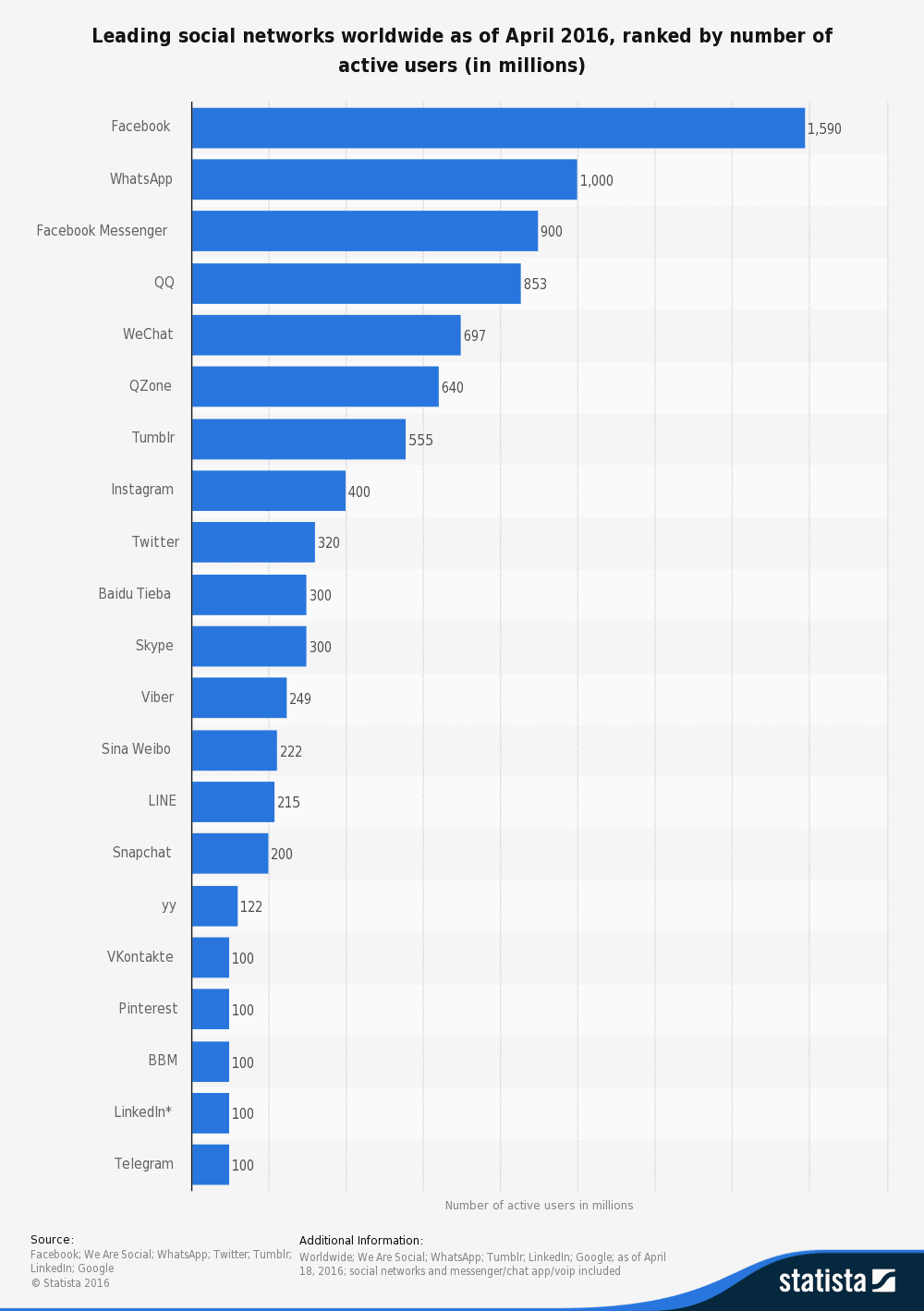
At this time Facebook is one of the most popular social medias at 1,590 million monthly active users, just behind that is an App called WhatsApp, a free messaging App, at 1,000 million monthly active users. Another very popular social media is Instagram coming in with 400 million monthly active users. Of course there are many other platforms and there is crossover, people who use multiple types of apps and media, but this gives us a glimpse at how many people use social media. The numbers of how many people use social media changes by magnitudes depending on how you define social media, for example some people don't see gaming platforms as a kind of social media, but you use these platforms to share videos and pictures to compare statistics to talk to friends, and make new ones. This being said Xbox Live has 48 million users, and PlayStation Network™ with 110 million, now compared to the titan of Facebook that's not much but it adds up it makes a big dent.
I briefly mentioned Instagram earlier, Instagram is interesting from a statistical point of view. Instagram does not have the most active users, however per 1000 users Instagram has the highest participation rate at 60-70 interactions per day per 1000 users over a 6 month period. With Facebook, Linkedin, and Twitter all coming in under 8 interactions per day per 1000 users over a 6 month period. This shows that though Instagram is not the most widely used app or social media platform, those who do use it are much more engaged not just silently watching. There are many more stats I could bore you with, however this section is meant to give you an idea of the magnitude of social media.
What is Covered in this Textbook
This is an open access textbook and is intended for a broad audience, especially college students who need this information for a class. A variety of topics are discussed including social media's impact on journalism, politics, personal and professional identity, perceptions and stereotypes, education, and as a professional tool. Here is a summary of each topic:
Origins of Memes: Contributors and Cause:
This chapter discusses the importance of the internet meme and it's contribution to youth culture. There is significance to the origins of the term “meme” and the application of it in history. Knowing who the creators of these memes are is also imperative in understanding the contemporary use of them. This chapter will also delve into why they are interwoven with youth culture and its impact on business marketing and internet culture.
Marketing and Entertainment in the Modern World of Social Media:
This chapter's focus is on how social media has supplied new ways for companies to reach out to both existing customer bases and potential new customers. Social media, is in fact, greatly important to any company that wants to see sustained success and relevancy to consumers. This chapter is about the ways companies create social media personalities that interact with people and how entertainment and storytelling promotes products; it also hits on how social media has created opportunities that negatively impact companies and how they are unique to the use of social media as marketing and/or advertisement "gimmicks."
Social Media's Role in Education:
Social media can be an excellent tool to connect with peers and professionals. This chapter discusses social media's role in education and learning management systems (LMS) that different educational institutions use. LMS are not just a platform for course work and grades, but they also include functions to connect with others associated with the course.
Social Media and Professionalism:
Social media is an excellent platform to network with professionals around the world. It is a personal branding tool and can create many benefits when used correctly. This chapter outlines the benefits of using social media for our professional life.
Social Media's Role in Politics:
This chapter discusses how Social Media is being used by people to engage in politics. This chapter delves into how social media is being used to encourage young voters to be engaged in political discussion and specifically how presidential candidates have used social media in recent elections to engage with there voters.
Social Media's Impact on Journalism:
This chapter discusses the impact that social media has had on journalism. It used to take some time between an event occurring and news getting out to people who were not there to witness it. Now, social media has created a platform to share news as it is happening so everyone can experience it, regardless of where they are or what they are doing.